Pest problems rarely happen overnight. Behind every visible infestation is a biological process that unfolds over time. Understanding the lifecycle of common pests is one of the most effective ways to manage and prevent infestations. When timing aligns with pest behavior and development stages, control efforts become more precise, efficient, and long-lasting. This is why timing matters so much in pest management.
By learning how pests grow, reproduce, and spread, homeowners and property managers gain valuable insight into when pests are most vulnerable. A lifecycle-based approach shifts pest control from guesswork to strategy, helping reduce infestations before they become widespread problems. Click Here to access more information.
Why Pest Lifecycles Are Important
Every pest species follows a lifecycle made up of distinct stages. These stages determine how pests behave, where they hide, and how quickly populations can grow. Some pests multiply rapidly, while others develop more slowly but live longer.
Understanding these patterns allows for better planning and prevention. When pest control efforts are timed correctly, they interrupt reproduction cycles and prevent pests from reaching damaging population levels.
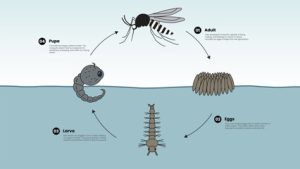
The Four Main Stages of Pest Development
Most common pests go through four primary stages of development: egg, immature stage, mature stage, and reproduction. While the exact appearance and duration of each stage may vary, the overall structure is similar.
Each stage presents different challenges and opportunities for control. Eggs are often hidden, immature pests may be less mobile, and mature pests are typically responsible for spreading and reproduction. Effective timing targets the stages where pests are easiest to manage.
Egg Stage: The Hidden Beginning
The egg stage is the foundation of any infestation. Eggs are often laid in protected areas where they are difficult to detect. Because eggs are stationary and well-hidden, they can go unnoticed until they hatch.
Timing matters at this stage because addressing conditions that support egg-laying can prevent future infestations. Reducing shelter, managing moisture, and eliminating food sources help disrupt the earliest phase of pest development.
Immature Stage: Rapid Growth and Vulnerability
Once eggs hatch, pests enter an immature stage marked by rapid growth. During this phase, pests focus on feeding and development. They may be smaller and less visible, but they are often more vulnerable to control efforts.
Targeting pests during this stage can significantly reduce population growth. Preventive strategies are especially effective here, as they limit resources and interfere with development before pests reach maturity.
Mature Stage: Mobility and Expansion
The mature stage is when pests become most noticeable. Fully developed pests are mobile, capable of spreading throughout a property, and responsible for reproduction. This stage often triggers visible signs of infestation.
Timing control efforts at this point is still important, but it can be more challenging. While mature pests are easier to identify, they are often more resilient. Early intervention in earlier stages helps prevent pests from reaching this phase.
Reproductive Stage: Population Explosion
Reproduction is the stage that drives infestations. Once pests begin reproducing, populations can grow rapidly. Some pests produce multiple generations within a short period, making timing critical.
Interrupting the reproductive stage is essential for long-term control. Strategies that prevent pests from reaching maturity or reduce their ability to reproduce can stop infestations from escalating.
How Environmental Conditions Affect Pest Lifecycles
Environmental factors play a significant role in how quickly pests move through their lifecycles. Temperature, humidity, and food availability all influence development speed. Warmer conditions often accelerate growth, while limited resources can slow it down.
Understanding these influences helps predict periods of increased pest activity. Timing pest management efforts to align with favorable conditions reduces the likelihood of sudden infestations.
Seasonal Patterns and Lifecycle Timing
Seasonal changes directly affect pest behavior and lifecycle progression. Some pests are more active during warmer seasons, while others seek shelter during cooler periods. These patterns create predictable cycles of activity.
By recognizing seasonal trends, pest control efforts can be planned proactively. Addressing pest risks before peak activity periods increases effectiveness and reduces the need for reactive measures.
Why Timing Improves Pest Control Results
Timing is not just about when pests are visible. It is about acting when they are most vulnerable. Lifecycle-based timing allows for targeted strategies that require less effort and deliver better outcomes.
When control measures align with pest development stages, they disrupt growth and reproduction more efficiently. This reduces the overall pest population and limits future infestations.
The Role of Monitoring in Lifecycle-Based Control
Effective timing relies on accurate monitoring. Observing pest activity, tracking changes, and noting seasonal patterns provide valuable information. Monitoring helps identify which lifecycle stage pests are currently in.
With this knowledge, control efforts can be adjusted accordingly. Monitoring turns pest management into an informed process rather than a reactive response.
Preventive Measures That Target Early Stages
Prevention is most effective when it focuses on the earliest lifecycle stages. Managing environmental conditions that support egg-laying and immature development reduces pest success from the start.
Cleaning, moisture control, and structural maintenance all play a role. These measures limit the resources pests need to complete their lifecycles.
How Poor Timing Leads to Persistent Infestations
Mistimed pest control efforts often fail to address the root of the problem. Treating only mature pests without disrupting reproduction allows populations to rebound quickly.
This cycle of temporary relief followed by reinfestation highlights why timing matters. Without addressing lifecycle stages strategically, pest problems tend to persist.
Lifecycle Knowledge and Long-Term Prevention
Understanding pest lifecycles supports long-term prevention. Instead of focusing solely on immediate results, this approach emphasizes sustainable solutions.
By anticipating pest behavior and acting at the right time, property owners can maintain consistent protection. Lifecycle awareness transforms pest control into a proactive practice.
Indoor and Outdoor Lifecycles
Many pests move between indoor and outdoor environments during different lifecycle stages. Eggs or immature pests may develop outside, while mature pests seek indoor shelter.
Recognizing this movement is essential for effective timing. Coordinating indoor and outdoor prevention ensures that all stages of the lifecycle are addressed.
The Impact of Timing on Property Protection
Pests can cause damage when allowed to complete their lifecycles unchecked. Early intervention prevents pests from reaching stages where they can harm structures, belongings, or landscaping.
Timing pest control efforts to stop development early protects property and reduces repair risks. Prevention at the lifecycle level safeguards long-term value.
Adapting Strategies to Different Pest Lifecycles
Not all pests develop at the same pace. Some complete their lifecycles quickly, while others take longer. Effective pest management adapts to these differences.
Understanding lifecycle variations ensures that timing strategies remain effective across different pest types. Flexibility and awareness are key to success.
Why Education Improves Timing Decisions
Knowledge empowers better decision-making. Learning about pest lifecycles helps property owners recognize early warning signs and act promptly.
Education reduces reliance on guesswork and improves confidence in preventive efforts. Informed timing leads to more reliable outcomes.
Integrating Lifecycle Timing Into Regular Maintenance
Lifecycle-based pest control works best when integrated into routine property care. Regular inspections, cleaning, and maintenance naturally align with lifecycle monitoring.
This integration creates a seamless approach to pest prevention. Timing becomes part of everyday property management rather than an occasional task.
The Long-Term Benefits of Lifecycle-Based Pest Control
Focusing on pest lifecycles delivers lasting benefits. Reduced infestations, lower costs, and improved living conditions are all outcomes of well-timed strategies.
Over time, lifecycle-based pest control builds resilience against recurring problems. Consistent timing prevents pests from gaining a foothold.
Why Timing Matters More Than Ever
Modern living environments offer pests plenty of opportunities to thrive. Understanding lifecycles and acting at the right time is more important than ever for effective control.
Timing transforms pest management from a reaction into a strategy. It ensures that efforts are efficient, targeted, and sustainable.
The lifecycle of common pests holds the key to effective pest control. Each stage presents unique challenges and opportunities, and timing determines success. By understanding how pests develop and when they are most vulnerable, property owners can take proactive steps to prevent infestations.
Lifecycle-based pest control is not about quick fixes. It is about informed, well-timed action that delivers long-term protection. When timing matters, knowledge makes all the difference.